Theme: Evolving the new methods for curing the parasitic diseases
Parasitology 2019
Parasitology & Microbes-2019 is a premier forum to analyze recent innovations and challenges in the field of Microbes & Parasites. Parasitology & Microbes-2019 welcomes students, speakers, presenters, and exhibitors from across the world to Tokyo, Japan on December 02-03, 2019. Parasitology and Microbiology are a risk and is considered a danger to most of laboratories or hospitals and they mostly deal with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of pathogenic diseases caused by microorganisms. As microbes nearly affect all activities of our life like, food, clothing, shelter, health hygiene etc., microbiology has made vast progressive steps in all these fields in little less than a century to improve the quality of our life. It has become increasingly important to human society. It has emerged as one of the most important and vital branches of life sciences. Infectious diseases have almost been conquered by new drugs, quality of agricultural crops improved by using techniques of genetic engineering, new varieties of wines, liquors have been produced- all these are possible only because of microbiology. All these advancements will make us wonder how our life would have been without the knowledge of Parasitology.
Parasitology can also be integrated into Microbiology as a science of studying various clinical applications of microbes for the enhancement of health and development of human life. Microbial diseases caused by pathogens may be exogenous or endogenous. In microbiology laboratory, cultures are the primary method used for isolating infectious diseases for study in the laboratory. Tissue or fluid samples are tested for the presence of a specific pathogen, which is determined by growth in a selective or differential medium.
Microbial diagnosis involves microbial culture, microscopy, biochemical tests and genotyping. Other less common techniques (such as X-rays, CAT scans, PET scans or NMR) are sometimes used to produce images of internal abnormalities resulting from the development of an infectious agent. Once an infectious disease has been diagnosed and identified, suitable treatment options must be evaluated by the physician and consulting medical microbiologists. Clinical Infectious diseases are treated with anti- bacterial (often called antibiotics) whereas fungal and viral infections are treated with antifungals and antivirals respectively. A broad class of drugs known as anti-parasitic are used to treat parasitic diseases. Clinical infections can be treated, and these treatments can be developed from microbes, as demonstrated by Alexander Fleming's discovery of penicillin as well as the development of new antibiotics from the bacterial genus Streptomyces among many others.
Why Japan?
Japan is the world's 4th largest island country and encompasses about 6,852 islands.Japan is an archipelago, or string of islands, on the eastern edge of Asia. There are four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu. There are also nearly 4,000 smaller islands, too! Japan’s nearest mainland neighbours are the Siberian region of Russia in the north, and Korea and China farther south. Japan is known worldwide for its traditional arts, including tea ceremonies, calligraphy and flower arranging. The country has a legacy of distinctive gardens, sculpture and poetry.
Market value
The Parasitology market in Asia Pacific for medical microbiology testing technologies will exhibit the highest market growth at a CAGR of 7.3%. High conversion rate from traditional testing methods to new advanced testing technologies is the key factors projected to trigger the market growth in APAC. The Asia Pacific region is also expected to lead product development and adoption of newer technologies. Improving economic conditions leading to increased purchasing power, increasing awareness regarding the benefit of testing technologies, and the presence of a large pool of patients suffering from various chronic diseases, the market is expected to grow at a double-digit rate.
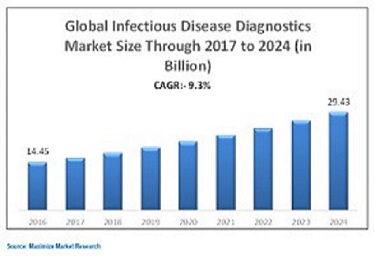
The Microbiology Market is projected to reach USD 5.77 Billion by 2021 from USD 3.35 billion in 2016, at a CAGR of 11.5%, during the duration 2016 to 2021. On the basis of product, the clinical microbiology market is categorized into gram strainers, bacterial colony counters, incubators, autoclave sterilizers, , anaerobic culture systems, microbial air samplers, petri dish fillers, blood culture systems, microbial culture systems which come under laboratory instruments and other laboratory instruments and such as microscopes, molecular diagnostic instruments, and mass spectrometers and reagents like pathogen specific kits and general reagents which are categorized as microbiology analyzers. The instruments sector is expected to account for the larger share of the global clinical microbiology market than the reagents sector in 2016. However, reagents sector is predicted to grow faster than the instruments sector, growing at a double-digit CAGR during 2016–2021. Growth in the reagents sector is largely driven by growing trend of reagent rental agreements (along with instrument sales) by prominent reagent manufacturers, raising private-public funding for researches on specific infectious diseases, increasing market obtainability of pathogen-specific kits across the globe, and growing demand for specific clinical microbiology reagents during widespread epidemic outbreaks.
Growth rate for drug discovery technologies
The growth rate for drug discovery technologies reached nearly $39.9 billion and $46.8 billion throughout the years 2013 and 2014. However, this market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.3% to nearly $79.5 billion during the period of 2014-2019. Furthermore, this market is poised to grow at a CAGR of around 12.2% over the next decade and will reach approximately $160 billion by 2025. The global systemic growth of antibiotics, its technologies and global market reached nearly $44.7 billion in 2020 from nearly $40.6 billion in 2015 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.0% from 2015 to 2020. The Pharmacy Automation, Technologies and Global Markets, its global inpatient and outpatient market has grown to nearly $3.8 billion in 2016 from $3.5 billion in 2015. This market is projected to grow at a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.9% from 2016 to 2021, increasing to $5.5 billion in 2021.
Global market in microbiology
The consumables, equipment and technology markets in the microbiology industry totaled nearly $7.7 billion in 2012. This total is expected to rise from $8.5 billion in 2013 to an exceptional rise of $11.4 billion in 2018, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% for the five-year period, 2013 to 2018.
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 1: Basic Parasitology
This session tracks covers Parasitism and Symbiosis. The Microenvironment and the Phases of Parasitism. Immunity to Parasites. Introduction to the Parasitic Protozoa. Sarcodina and Opalinata: The Amoebae and Opalinids. Apicomplexa, Microspore, Ascetospora, and Myxozoa. Ciliophoran: The Ciliates. Introduction to the Symbiotic Flatworms. Monogenea: The Monogenetic Trematodes. Digenea: The Digenetic Trematodes. Cestoidea: The Taperworms. Cestrodaria: The Unsegmented Tapeworms. Eucestoda: The True Tapeworms. Acanthocephala: The Spiny-Headed Worms. Nemata: The Roundworms Adenophorean Nematodes.
Secernentean Nematodes Physiology and Biochemistry of Nematodes. Introduction to the Parasitic Arthropods. The Mites. Introduction to the Parasitic Insects. Diptera: The Flies, Gnats, and Mosquitoes. Hemiptera: The True Bugs. Hymenoptera: The Wasps. Coleoptera: The Beetles. Strepsiptera: The Twisted-Wing Insects. Other Zooparasites.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019:7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 2: Animal Associations
Animals have constant interaction with other organisms. The interactions can be classified into two types:
1. Intra-specific interactions
2. Inter-specific interactions
Intra-specific interactions occur between organisms of same species.
They range between relatively loose associations between members of flock of speed, to highly complex interactions seen in colonial invertebrates. E.g.: Bryozoans.
Inter-specific interactions occur between different species of organisms. The degree of association can be varying between being extremely loose to highly complex.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 3: Parasitic Hosts
Parasitism is a non-mutual symbiotic relationship between species, where as one species the parasite benefits at the expense of other the host. Traditionally parasite referred primarily to organisms visible to the naked eye or macro parasites such as helminths.
Parasites can be micro parasites, which are typically smaller such as protozoa viruses, and bacteria.
Parasites typically do not kill their host but generally much smaller than their host and will often live in or on their host for an extended period. Parasitism differs from the parasitoid relationship in that parasitoids generally kill their hosts.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 3: Therapeutic Parasitology
Medical parasitology traditionally has included the study of three major groups of animals: parasitic protozoa, parasitic helminths (worms), and those arthropods that directly cause disease or act as vectors of various pathogens. A parasite is a pathogen that simultaneously injures and derives sustenance from its host. Some organisms called parasites are actually commensals, in that they neither benefit nor harm their host (for example, Entamoeba coli). Although parasitology had its origins in the zoologic sciences, it is today an interdisciplinary field, greatly influenced by microbiology, immunology, biochemistry, and other life sciences.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 5: Protozoology
This session covers protozoa which infect humans. The basic biology of these protozoa, as well as the clinical manifestations of the diseases they cause, will be discussed.
Life cycles, morphological features, host-parasite interactions, geographical distribution, reservoir hosts, methods of transmission and control, pathology, immunological aspects and diagnosis will be covered. The biological and clinical perspectives gained in this course will assist students in the recognition, evaluation and management of public health problems or clinical practice involving medically important protozoa.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 6: Helminthology
Medical helminthology is the field of medicine that pertains to helminths (worms) capable of disease in people.
The public health impact of medical helminths is appreciable. Two billion people are infected by soil-transmitted helminths such as Ascaris, hookworms, and Trichuris trichiura and by schistosomes. Early childhood infections by soil-transmitted helminths delays physical and cognitive development. Other widespread helminthic infections include onchocerciasis, lymphatic filariasis, dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease), and food-borne trematode and tapeworm infections. All of these infections cause chronic morbidity and debilitation.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 7 Experimental Parasitology
Parasites require different cultivation Practice such as nutrients, temperature and even incubation conditions. Cultivation is an important method for diagnosis of many clinically parasites. eg:Entamoeba histolytica, Trichomonas vaginalis, Leishmania spp., Strongyloides stercoralis and free-living amoebae.
The parasitic infections, culture are not a routine identification technique. Useful for clinching the diagnosis in some protozoan parasitic infections, e.g. in case of Central Nervous System infections by frees living amoebae.
Parasite cultivation can be used to study the biochemistry, physiology, and metabolism of the parasites. Determine their nutritional requirements, and for understanding their ultra-structural organization, life-cycle and host-parasite cell-mediated protective systems against the parasites.
Cultivating parasites helps in differentiating clinical isolates. The techniques are iso-enzyme electrophoresis, monoclonal antibody techniques, and DNA probe techniques can be easily applied on cultures.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 8 Arthropod Parasites
Arthropods form a huge assemblage of small fluid-filled cavity within the body of most multicellular animals with jointed limbs. They exhibit segmentation of their bodies which is often masked in adults because of their 10-25 body segments which are combined into 2-3 functional groups called tagmata. They exhibit varying degrees of cephalization, sensory receptors and feeding structures in the head region.
Arthropods possess a rigid cuticle shape exoskeleton consisting mainly of proteins and chitin. The exoskeleton is usually hard and insoluble which is indigestible and impregnated with calcium salts. The exoskeleton provides physical and physiological protection .Skeletal plates are joined by flexible articular membranes and the joints can be called as hinges or pivots made from chondyles and sockets.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 9 Anatomical Parasitology
Structural parasitology is the study of structures of parasitic proteins. Among protozoan parasites, the phylum of Apicomplexa includes organisms responsible for malaria, toxoplasmosis and cryptosporidiosis. Trypanosoma and Leishmania parasites, belonging to the phylum of Kinetoplastida, cause Chagas disease, African Sleeping Disease and visceral leishmaniasis. For some of these diseases, such as malaria, existing drugs face the threat of resistance. For others, such as cryptosporidiosis, there is no effective chemotherapy.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track:10 Veterinary Parasitology
This session track covers the study of animal parasites, especially relationships between parasites and animal hosts. Parasites of domestic animals, (livestock and pet animals), as well as wildlife animals are considered. Veterinary parasitologists study the genesis and development of parasitoses in animal hosts, as well as the taxonomy and systematics of parasites, including the morphology, life cycles, and living needs of parasites in the environment and in animal hosts. Using a variety of research methods, they diagnose, treat, and prevent animal parasitoses. Data obtained from parasitological research in animals helps in veterinary practice and improves animal breeding. The major goal of veterinary parasitology is to protect animals and improve their health, but because a number of animal parasites are transmitted to humans, veterinary parasitology is also important for public health.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 11 Transmission of Parasitic Infection
The Parasitic Disease can also be known as parasitosis, infectious disease can be caused or transmitted by a parasite. Many parasites do not cause diseases. Parasitic diseases can affect practically all living organisms, including plants and mammals. The parasites like Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium spp. can cause disease directly, but other organisms can cause disease by the toxins that they produce.
Common ways for the transmission of Parasites
Food or Water Contamination - roundworm, amoebae, giardia, cryptosporidium
Vectors
mosquito - canine heartworm, filaria, malaria
flea - canine tapeworm
housefly - amoebic cysts
sand fly - leishmaniasis
Sexual Contact - trichomonas, giardia, amoebae
Inhalation of Contaminated Dust or Air - pinworm, Toxoplasma gondii
Skin Penetration - hookworms, schistosomes, strongyloides
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 12 Immunoparasitology
The main topics covered are the physiology, immunology, biochemistry, and molecular biology of eukaryotic parasites, and the interaction between the parasite and its host, including chemotherapy against parasites.
The diseases caused by these parasites constitute major human health problems throughout the world. The incidence of many parasitic diseases (eg. schistosomiasis, malaria) have increased rather than decreased in recent years. Other parasitic illnesses have increased in importance as a result of the AIDS epidemic (eg., cryptosporidiosis, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, and strongyloidiasis).Like other pathogens, parasites must survive in the face of a highly potent immune system. Over millions of years of evolution, they succeed in this through a great diversity of strategies for avoiding immune detection, suppressing cellular immunity and deflecting immune attack mechanisms.
Similarly hosts have evolved resistance in various ways to overcome their entry and existence. Host- parasite interactions provide fascinating examples of evolutionary 'arms-races' in which the immune system plays a key role. The main topics covered are the physiology, immunology, biochemistry, and molecular biology of eukaryotic parasites, and the interaction between the parasite and its host, including chemotherapy against parasites.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 13 Tested Parasitology
The effects of parasitic worms on the immune system are a recently emerging topic of study among immunologists and other biologists. Experiments involved a wide range of parasites, diseases and hosts. The effects on humans have been of special interest for the researchers. The tendency of many parasitic worms to pacify the host's immune response allows them to mollify some diseases while some worsening others.
Extensive research shows that parasitic worms have the ability to deactivate certain immune system cells, leading to a gentler immune response. Anthelmintics are drugs that are used to treat infections with parasitic worms.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 14 Equatorial Parasitology
This scientific session covers many infections and infestations that are classified as "tropical diseases" used to be endemic in countries located in the tropics. This includes widespread epidemics such as malaria; Ebola and hookworm infections as well as exceedingly rare diseases like lagochilascaris minor. Many of these diseases have been controlled or even eliminated from developed countries, as a result of improvements in housing, diet, sanitation, and personal hygiene.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 15 Scientific Manifestations of Parasitic Diseases
Parasites are single cell small sized micro-organisms that live on other living things including animals and humans to get food and survive. Sometimes humans can suffer severe life threatening infections when they have a parasitic attack. Parasitic diseases caused mainly by Protozoa and Helminths.
Parasites are of two types’ ectoparasites and endoparasites. If any parasite lives on the surface of a host such as human it is called as ectoparasite and parasite lives inside the living thing it is called as endoparasite. Mainly parasitic diseases are occurred by endoparasites.
The common parasitic diseases are Dysentery, Pneomonia, Filariasis, Scabies, and Pediculosis etc.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Tracks 16: Cataloging of Parasites
Then laboratory diagnosis involves conventional methods such as optical microscopy used for the morphological identification. Molecular biology techniques are used to diagnose parasite structures, identification and characterization of parasites. The objective of the present study was to review the main current and new diagnostic techniques for Identification of parasite infections.
E.g: polymerase chain reaction (PCR), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), Luminex xMAP, real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), Molecular assays have comprehensively assisted in the diagnosis treatment and epidemiological studies of parasitic diseases.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 17: Benefits of Parasites
Parasites are the potential key for treating autoimmune diseases. There is a new weapon in the fight for against autoimmune diseases such as Type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease. The common trait is that an immune system that attacks its own organs and tissues.
Helminthic therapy is an experimental type of immune therapy, and it is the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune disorders.
Helminths are parasitic worms such as hookworms, whipworms, and threadworms that live within a host organism on which they rely for the nutrients. The WHO estimated that a staggering 2 billion people suffering from worm infections.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 18 Epidemiology of Bacterial Infections
Medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology are focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis.
Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behaviour, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety, finally in current situation related to one health approach mostly health policy makers recommends to widely applicability of medical entomology for disease control efficient and best fit on achieving development goal and to tackle the newly budding zoonotic diseases.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 19 Nourishment and Biochemistry of Parasites
Parasitic nutrition is a mode of heterotrophic nutrition where an organism lives on the body surface or inside the body of another type of organism .The parasite obtains nutrition directly from the body of the host. The parasites derive their nourishment from their host. This symbiotic interaction is often described as harmful to the host. Parasites are dependent on their host for survival; host provides nutrition and protection for the parasite. As a result of this dependence, parasites have considerable modifications to optimise parasitic nutrition and therefore their survival.
Parasites require nutrients to carry out essential functions including reproduction and their growth. The nutrients required from the host are, amino acids, carbohydrates and lipids. Carbohydrates are utilised to generate energy, amino acids and fatty acids are involved in the synthesis of macromolecules and the production of eggs. Most parasites are heterotrophs, so they are unable to synthesise their own 'food'.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 20 Recombinant DNA Technology on Parasitology
Recombinant DNA technology has major impact on our understanding of many organisms and biological processes over the past three decades. The polymerase chain reaction has greatly enhanced the power of recombinant DNA by provided allowance for the detection of a little as one molecule. Cloned complementary DNA copies of mRNAs are easy to expression of individual gene products in other organisms.
The isolation of malaria antigen by expression screening cDNA, have been widely used in the fields of parasitology.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 21 Analysis and Limitation of Parasitic Diseases
The control of parasitic diseases of humans has been undertaken since the cause and history of the infections was recognized. Some parasitic infections such as malaria have proved difficult to control. Helminth infections can be effectively controlled.
They are different approaches to control from diagnosis to treatment of parasitic diseases. To control the transmission by preventative chemotherapy and vector control. Then fact that the spread of many parasitic diseases is by contaminated supplies resulting from inadequate waste disposal.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 22 Vector-borne Diseases
Vectors are living organisms that can transmit infectious diseases between humans or from animals to humans. Many of these vectors are bloodsucking insects, which ingest disease-producing microorganisms during a blood meal from an infected host (human or animal) and later inject it into a new host during their subsequent blood meal.Mosquitoes are the best known disease vector. Others include ticks, flies, sandflies, fleas, triatomine bugs and some freshwater aquatic snails.
Vector-borne diseases are illnesses caused by pathogens and parasites in human populations. Every year there are more than 1 billion cases and over 1 million deaths from vector-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue, schistosomiasis, human African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis and onchocerciasis, globally. Vector-borne diseases account for over 17% of all infectious diseases. Distribution of these diseases is determined by a complex dynamic of environmental and social factors.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track: 23 Molecular biology and Immune Evasion
This session covers the molecular biology and biochemistry of parasitic protozoa and helminths and their interactions with both the definitive and intermediate host. The main subject areas covered are:
•The structure, biosynthesis, degradation, properties and function of DNA, RNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and small molecular-weight substances
• Intermediary metabolism and bioenergetics
• Drug target characterization and the mode of action of antiparasitic drugs
• Molecular and biochemical aspects of membrane structure and function
• Host-parasite relationships that focus on the parasite, particularly as related to specific parasite molecules.
• Analysis of genes and genome structure, function and expression
• Analysis of variation in parasite populations relevant to genetic exchange.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Track 24: Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases
Tick-borne diseases are becoming a serious problem in this country as people increasingly build homes in formerly uninhabited wilderness areas where ticks and their animal hosts live. Tickborne diseases can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Most people become infected through tick bites during the spring and summer months.
Tick-borne diseases can be found throughout the United States. For example, Lyme disease, first discovered in Connecticut in the early 1970s, has since spread to every state except Hawaii.
Ticks transmit ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis, both bacterial diseases. Babesiosis is caused by parasites carried by deer ticks. These diseases are found in several states.Tularemia, a less common tick-borne bacterial disease, can be transmitted by ticks as well as other vectors (carriers) such as the deerfly. Public health experts are concerned that the bacterium that causes tularemia (Francisella tularensis) could be used as a weapon of bioterrorism.
Related Conferences:
ICPID 2019: 7th Annual Conference on Parasitology & Infectious Diseases, November 18-19, 2019; ICPM 2019, Johannesburg, South Africa; 6th International Conference on Parasitology & Microbiology July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands; ICMC: 3rd International Conference on Medical and Clinical Microbiology May 01-02, 2019 | ANA Crowne Plaza | Kyoto, Japan; 4th International Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes May 20-21, 2019 Tokyo, Japan; 12th Annual Meet on Bacteriology & Applied Microbiology September 23, 24 2019 | Radisson Hotel Narita | Tokyo, Japan
Parasitology Conferences | Parasitology Congress | Microbiology Conference | Parasitology 2019
Conference Highlights
- Basic Parasitology
- Parasitic Host
- Therapeutic Parasitology
- Helminthology
- Experimental Parasitology
- Arthropod Parasites
- Anatomical Parasitology
- Transmission of Parasitic Infection
- Immunoparasitology
- Tested Parasitology
- Equatorial Parasitology
- Scientific Manifestations of Parasitic Diseases
- Cataloging of Parasites
- Benefits of Parasites
- Epidemiology of Bacterial Infections
- Nourishment and Biochemistry of Parasites
- Recombinant DNA Technology on Parasitology
- Analysis and Limitation of Parasitic Diseases
- Vector-Borne Diseases
- Molecular Biology and Immune Evasion
- Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | December 02, 03 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | ||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Bacteriology & Parasitology
- Journal of Molecular & Biochemical parasitology
- Journal of Medical Microbiology & Diagnosis
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by





















